Filtro de Jeringa(Mixed Cellulose)
-
Filtro de jeringa (también llamado filtro-rueda si tiene la forma de rueda) es un cartucho de filtro de un solo uso, que se fija al extremo de una jeringa. Filtros de jeringa pueden tener conectores para cierre Luer, pero que no universalmente. Uso de aguja es opcional; cuando sea necesario, puede colocarla al extremo del filtro de jeringa.
-
Filtro de jeringa normalmente consiste de una carcasa de plástico con membrana que sirve como un filtro. Si un líquido exige depuración, tírelo a través de una jeringa o exprímalo hacia fuera de una jeringa a través de un filtro.

Características del producto+
|
MCE13022 |
Filtro de Jeringa, 13mm, 0.22um, Selulosa Mixta |
|
MCE13045 |
Filtro de Jeringa, 13mm, 0.45um, Selulosa Mixta |
|
MCE17022 |
Filtro de Jeringa, 17mm, 0.22um, Selulosa Mixta |
|
MCE17045 |
Filtro de Jeringa, 17mm, 0.45um, Selulosa Mixta |
|
MCE25022 |
Filtro de Jeringa, 25mm, 0.22um, Selulosa Mixta |
|
MCE25045 |
Filtro de Jeringa, 25mm, 0.45um, Selulosa Mixta |
|
MCE30022 |
Filtro de Jeringa, 30mm, 0.22um, Selulosa Mixta |
|
MCE30045 |
Filtro de Jeringa, 30mm, 0.45um, Selulosa Mixta |

Technical Information+
Vial Finish Specifications
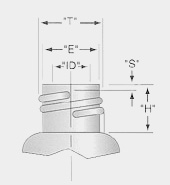
- Andard Screw Thread Finish
- "T" = Outer diameter of the thread
- "E" = Inside diameter of the thread
- "ID" = Inside diameter
- "S" = Start of thread
- "H" = Distance from top of finish to shoulder for closure clearance

- Andard Screw Thread Finish
- "T" = Outer diameter of the thread
- "E" = Inside diameter of the thread
- "ID" = Inside diameter
- "S" = Start of thread
- "H" = Distance from top of finish to shoulder for closure clearance
Screw Thread Finishes
-
GPI refers to the "Glass Packaging Institute"
-
The GPI is responsible for establishing and issuing standards for the types and finishes produced by American glass manufacturers.
-
GPI refers to the "Glass Packaging Institute"
-
The GPI is responsible for establishing and issuing standards for the types and finishes produced by American glass manufacturers.
-
GPI refers to the "Glass Packaging Institute"
-
The GPI is responsible for establishing and issuing standards for the types and finishes produced by American glass manufacturers.
-
GPI refers to the "Glass Packaging Institute"
-
The GPI is responsible for establishing and issuing standards for the types and finishes produced by American glass manufacturers.
Typical GPI finishes found in the chromatography field are as follows:
Glass Technical Information
-
Borosilicate - A glass that is high in silicate and having at least 5% boron oxide.
-
Linear Coefficient of Expansion - Fractional change in length of glass per degree change in temperature.
-
Strain Point - Maximum temperature to which glass should be heated during use"
-
USP Type - Pharmaceutical glass containers can be classified as USP Type I, II, III or NP.
-
Type I - Borosilicate glass represents the least reactive glass.
-
Type I glass has the least pH shift. (Lowest leaching characteristics) Coefficient of Expansion = 33 or 51 for Clear and 51 for Amber
-
Type II - is de-alkalized soda lime glass with higher levels of sodium hydroxide and calcium oxide.
-
Type III - soda lime glass - cannot be autoclaved.
-
Type NP - general purpose soda-lime glass used where chemical durability and heat shock are not factors.
-
Coefficient of Expansion = 92.
Types of Glass:
GLASS PROPERTIES
| Color |
Clear |
Amber |
|---|---|---|
|
Linear Coefficient of Expansion |
33 |
51 |
|
Strain Point (Degrees Celsius) |
515 |
535 |
|
USP Class Type |
Type 1 |
Type 1 |
|
Light Protection |
No |
Yes |
Plastic Properties
| Type of Plastic | Type of Plastic | Type of Plastic | Type of Plastic | Type of Plastic | Type of Plastic |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum use temperature, C/F | 80°C/176°F | 80°C/176°F | 80°C/176°F | 80°C/176°F | 80°C/176°F |
| Maximum use temperature, C/F | 80°C/176°F | 80°C/176°F | 80°C/176°F | 80°C/176°F | 80°C/176°F |
| Maximum use temperature, C/F | 80°C/176°F | 80°C/176°F | 80°C/176°F | 80°C/176°F | 80°C/176°F |
| Maximum use temperature, C/F | 80°C/176°F | 80°C/176°F | 80°C/176°F | 80°C/176°F | 80°C/176°F |
| Maximum use temperature, C/F | 80°C/176°F | 80°C/176°F | 80°C/176°F | 80°C/176°F | 80°C/176°F |
PP* = Some radiation resistant polypropylene resins available.
**Flexibility - Depends on thickness.
Process Flow Diagram+
- STEP 01
The workers clean the tubing with cloth
- STEP 02
The workers plug the tubing into machine for making vials
- STEP 03
The vials are transferred to QC for Physical Test
- STEP 04
The workers put the tested vials into one big package (500-800pcs/pack)
- STEP 05
The workers get the vials from big package and put the vials into one special tray.
- STEP 06
Put the tray with vials into the Water injection machine
- STEP 07
The vials in tray will be transferred to next step for Ultrasonic oscillations.
- STEP 08
The vials in tray will be transferred to Jilt water machine.
- STEP 09
The vials in tray will be transferred to Infrared drying case.
- STEP 10
The workers will collect the vials after vials are dry.
- STEP 07
The vials in tray will be transferred to next step for Ultrasonic oscillations.
- STEP 11
The workers will check all the vials inclouding the bottom neck ,bottom ,inerts.
- STEP 12
The workers will pack 100pieces vials into one package.
- STEP 13
The workers will send the package to sealing machine for packing.
+
Consulta
Si usted tiene cualquier pregunta o comentario, éntrenos en contacto con por favor sin la vacilación. Le responderemos tan pronto como sea posible. ( * es la información requerida)



